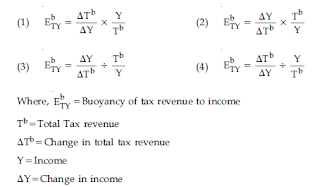1. Which of the following will be true for both monopoly and monopolistic competition in the short run?
(1) Price is greater than marginal revenue.
(2) Price is equal to marginal revenue.
(3) Price is equal to marginal cost.
(4) Price is equal to average cost.
2. Consider the following matrix which describes the respective strategies and the corresponding pay-offs of firms A and B operating in a duopoly:
Which of the following statement(s) is/are true for the above game?
Select the correct answer from the codes given below:
(a) Firm A has no dominant strategy.
(b) Firm B has a dominant strategy.
(c) The game has a Nash equilibrium.
(d) Neither Firm A nor Firm B has a dominant strategy.
Code:
(1) (a), (c)
(2) (b), (c)
(3) (d) Only
(4) (a), (b) and (c)
3. In the context of oligopoly, consider the following statements:
(a) Cournot’s equilibrium is a Nash equilibrium.
(b) Stackelberg equilibrium is a Nash equilibrium.
Select the correct answer from the code given below:
(1) Only (a)
(2) Only (b)
(3) Both (a) and (b)
(4) Neither (a) nor (b)
4. Match List – I with List-II and point out the correct answer from the codes below:
List - I (Concept)
|
List-II (Economist)
|
(a) Profit as a dynamic surplus
(b) Profit as a reward for innovation
(c) Profit as a reward for uncertainty bearing
(d) Profit arises due to monopoly power enjoyed by the producers
|
(i) J. Schumpeter
(ii) M. Kalecki
(iii) F.H. Knight
(iv) J.B. Clark
|
Code:
(a) (b) (c) (d)
(1) (ii) (i) (iii) (iv)
(2) (iv) (i) (iii) (ii)
(3) (iv) (ii) (iii) (i)
(4) (iii) (iv) (ii) (i)
5. When the marginal cost is equal to average cost, the slope of the average cost is:
(1) positive
(2) negative
(3) zero
(4) infinite
6. For the function Q=A ⋅ Kα ⋅ Lβ, which of the following is correct?
(1) The degree of homogeneity is 1
(2) The elasticity of substitution is equal to α+β
(3) Output elasticity with respect to capital is α
(4) The marginal product of a factor=Average product of the factor
7. When information asymmetry is observed after an agreement is obtained between individuals, it is called:
(1) Signaling
(2) Moral hazard
(3) None of the above
(4) Both (1) and (2) above
8. In the given diagram, after the price change, the price line shifts from PQ to PQ’. And consumer comes to equilibrium at point B instead of point A. Then what is true for potatoes?
(1) It is a normal good.
(2) It is an inferior good.
(3) It is a Giffen good.
(4) Nothing can be said about the nature of the good.
9. Which amongst the following is a correct description of inverse demand function?
(1) p=f (D)
(2) D=f (p)
(3) D = f(1/p)
(4) p = f(D, 1/y)
Where p=price, D=demand, and y=income.
10. The first fundamental Theorem of Welfare Economics requires:
(1) that there be an efficient market for every commodity.
(2) that the economy operates at some point on the utility possibility curve.
(3) producers and consumers to be price takers.
(4) All of the above.
11. The Theory in which the trade cycle is generated due to excess of actual over the desired investment has been given by who amongst the following?
(1) R.G. Hawtry
(2) F. Hayek
(3) P. Samuelson
(4) J. Schumpeter
12. Consider the following statements:
(a) ‘Liquidity trap ‘is a situation when people prefer to hold money rather than investing it.
(b) ‘Liquidity preference’ is the situation when people prefer to invest money rather than hold it.
(c) ‘Liquidity crunch’ is a situation of short supply of money in the money market.
(d) ‘Credit crunch’ is a situation of short supply of money in the loan market.
Select the correct statements using the code given below:
(1) (a), (b) and (d)
(2) (a), (c) and (d)
(3) (b), (c) and (d)
(4) (a), (b) and (c)
13. ‘Menu costs’ in relation to inflation refers to:
(1) Cost of revaluing the currency.
(2) Cost of altering price lists.
(3) Cost of the maintenance of monetary base.
(4) Cost of finding better rates of return.
14. According to M. Friedman, Quantity Theory of Money is the theory of:
(1) Value of money
(2) Price determination
(3) Nominal income
(4) Demand for money
15. Gilt-edged market means:
(1) Bullion Market
(2) The market of pure metals
(3) The market of government securities
(4) Market of commodities
16. Which of the following is likely to be most inflationary in its impact?
(1) Repayment of public debt
(2) Borrowings from the public to finance a budget deficit
(3) Borrowings from banks to finance a budget deficit
(4) Creating new money to finance a budget deficit
17. Consider the following statements regarding the Marginal Standing Facility (MSF).
(a) MSF is on the line of the existing LAF and is part of it.
(b) MSF is a costlier route than Repo.
(c) MSF functions as the last resort for banks to borrow short term funds.
(d) MSF is linked to the net demand and time liabilities of the Banks.
Choose the correct code given below.
(1) (b), (c) and (d)
(2) (a), (b) and (c)
(3) (a), (c) and (d)
(4) (a), (b), (c) and (d)
18. “The absorption approach” of analyzing the balance of payments was formulated by:
(1) M. Friedman
(2) Marshall and Lerner
(3) Sydney Alexander
(4) Haberler
19. Which amongst the following is not correctly matched with regard to the balance of payments account?
Item
|
Nature
|
(1) Import of goods and services
(2) Receipt of transfer payments
(3) Direct investment receipts
(4) Portfolio investment redemption
|
Debit in the current account
Credit in the current account Credit in the capital account Debit in the current account |
20. Prebisch – singer hypothesis relates to:
(1) Balance of payments problem of developing countries.
(2) Terms of trade in developing countries.
(3) Prevalency of poverty among developing countries.
(4) Inequality of income in developing countries.
21. Which of the following statement about India’s balance of payments is not correct?
(1) If a foreign citizen deposits some money in a bank in India, the accounts regard this as a credit.
(2) The current account balance shows only the balance for the trade in goods and services combined.
(3) Allowing for errors and omissions, the accounts always balance.
(4) If the country’s reserves of foreign currencies increase then there is a minus sign for this entry.
22. Let elasticity of demand for exports for a certain country be ex and elasticity of demand for imports be em. Assume that the country devalues its currency. Its balance of payments will almost certainly show improvement if:
(1) ex + em > 1
(2) ex + em < 1
(3) ex + em=1
(4) ex = em =1
23. Which of the following would cause Rupee to depreciate against U.S. Dollar, other things being equal?
(1) A rise in interest rates in India.
(2) A fall in incomes in the U.S.A.
(3) An expected rise in the external value of the rupee.
(4) An increased flow of foreign investment into India.
24. According to Mercantilists, trade is a:
(1) Positive sum game
(2) Infinite sum game
(3) Zero-sum game
(4) Negative sum game
25. There is incomplete specialization in production when the country faces:
(1) constant opportunity costs
(2) decreasing opportunity costs
(3) increasing opportunity costs
(4) indeterminate opportunity costs
26. Tax buoyancy is expressed as:
(1) 1
(2) 2
(3) 3
(4) 4
27. Income tax is generally based on the principle of:
(1) Benefit received principle
(2) Ability to pay principle
(3) Willingness to pay principle
(4) None of these
28. Which method can help in obtaining a welfare improvement if externalities exist?
(1) Regulation
(2) Assigning property rights and permitting bargaining
(3) Pigovian taxes
(4) All of the above
29. Which of the following is a capital receipt in the Government budget?
(1) Interest receipts on loans given by the Government to other parties.
(2) Dividend and profit of public enterprises.
(3) Borrowings of the government from the public.
(4) Property tax receipts.
30. Which amongst the following would be most effective in mitigating the effect of externalities?
(1) Fiscal policy
(2) Regulation of monopoly
(3) Active monetary policy
(4) Freeing the markets
31. The maximum social advantage is achieved when:
(1) Total Social Sacrifice=Total Social Benefits
(2) Marginal Social Sacrifice=Marginal Social Benefits
(3) Net Social Sacrifice=Net Social Benefits
(4) Average Social Sacrifice=Average Social Benefits
32. Statutory incidence of a tax deal with:
(1) the person(s) legally responsible for paying the tax.
(2) the amount of revenue left over after taxes.
(3) the amount of taxes paid after accounting for inflation
(4) the amount of tax revenue generated after a tax is levied.
33. The relationship described by the Expectations – Augmented Phillips curve is correct in which of the following?
(1) Only in the long run.
(2) Only in the short run.
(3) Both in the short run and in the long run.
(4) Neither in the short run nor in the long run.
34. Non Accelerating Inflation Rate of Unemployment (NAIRU) means:
(1) a rate of unemployment for which the change in the rate of inflation is zero.
(2) a rate of inflation which makes the rate of unemployment zero.
(3) a rate of inflation for which the change in the rate of unemployment is zero.
(4) a rate of unemployment which is equal to the rate of inflation.
35. New Keynesians use which of the following to explain price and wage stickyness?
(1) Staggered labor contracts
(2) Menu Costs
(3) Behavior-based on bounded rationality
(4) All of the above
36. Consider the following statements:
(a) Effective demand in a market is the demand for a product or service which occurs when purchasers are constrained in a different market.
(b) Notional demand is the demand that occurs when purchasers are not constrained in any market.
Which of the above statements is/are correct? Answer from the code below:
(1) Only (a) is correct
(2) Only (b) is correct
(3) Both (a) and (b) are correct
(4) Neither (a) nor (b) is correct
37. For the capitalist economy, the primary objective of New Classical Economics is to explain which of the following?
(1) Business cycle phenomenon
(2) Underemployment
(3) Wage – price rigidity
(4) Effectiveness of Government policy
38. Which of the following growth model(s) assume(s) Neutral Technical Progress?
(1) Harrod model
(2) Solow model
(3) Both (1) and (2)
(4) Neither (1) nor (2)
39. In an economy, the GDP deflator is found to be 110 for the current year. If the GDP has registered an annual growth rate of 15 percent in the same year, then, the rate of growths of real GDP will be:
(1) 5%
(2) 1.5%
(3) 25%
(4) 2.5%
40. What is the nature of equilibrium in the IS-LM model?
(1) Stock equilibrium
(2) Flow equilibrium
(3) Stock and flow equilibrium
(4) Oscillating equilibrium
41. If marginal propensity to import is 0.1 and the marginal propensity to consume is 0.7, the value of the income multiplier will be:
(1) 1.25
(2) 2.33
(3) 2.5
(4) 3.33
42. According to the neoclassical theory of distribution, constancy in the wage share in national income would come about only when the elasticity of factor substitution:
(1) is less than one
(2) is equal to one
(3) is zero
(4) is greater than one
43. Which amongst the following is not a feature of J.E. Meade’s model?
(1) Perfect competition prevails.
(2) The economy produces consumer goods and producer goods.
(3) Perfect substitution is possible between consumption and capital goods.
(4) It examines the relationship between the growth rate of population and the growth rate of savings.
44. Consider the following production function forms with a technical progress term A(t).
(a) Q=f (Kt, A(t) ⋅ Lt)
(b) Q=f (A(t) ⋅ Kt, Lt)
(c) Q=A(t) f (Kt, Lt)
Of the above, which production function, with labor augmenting technology will keep the distribution of output between labor and capital as constant? Answer from the code below:
(1) Only (a)
(2) Both (a) and (b)
(3) Only (c)
(4) Both (a) and (c)
45. Which of the following statements about the AK model (Y=AK) of growth is false?
(1) This is a part of endogenous growth theories.
(2) The model assumes that an increase in the physical stock of capital will shift the production function upwards.
(3) The model assumes diminishing returns to capital.
(4) The model suggests that if the level of investment is higher than depreciation, there would be sustained growth.
46. Which of the following is not a correct feature for the absolute convergence to hold good?
(1) The same population growth rate
(2) Same savings propensity
(3) Same capital-labor ratio
(4) Different capital-labor ratio
47. In Solow’s growth model, the output per capita is a function of:
(1) Labour – Output ratio
(2) Capital – Output ratio
(3) Technical progress
(4) Capital – Labour ratio
48. Dusenberry was of the opinion that less developed countries will have a serious and adverse effect on their balance of payments due to:
(1) demonstration effect
(2) multiplier effect
(3) backwash effect
(4) spread effect
49. Leibenstein in his critical minimum effort thesis treats the population as a factor that is:
(1) Income-generating
(2) Investment – inducing
(3) Income – depressing
(4) Market – expanding
50. ‘Workers must own the capital to which their savings has given rise.’ This is an important assumption of the growth model, developed by:
(1) L. Pasinetti
(2) N. Kaldor
(3) R. Solow
(4) J.E. Meade
**TO BE CONTINUED........